Food safety management system
When a facility has a functioning Food Safety Management System (FSMS), team members perform better, and customers will receive a consistent message when visiting.
In Maryland a HACCP plan is required for every moderate and high priority facility when they start up. Often, they become forgotten until a health inspector asks to review it. A HACCP plan should not be looked at as “just another requirement”. A well written HACCP plan should be part of your overall food safety management system and should be part of your day to day operations. However, HACCP is only the beginning of your full Food Safety Management System.
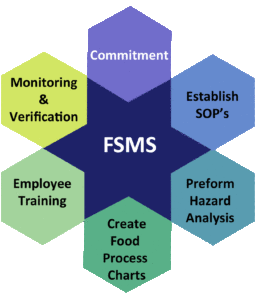
What is a FSMS?
The short answer is; Team members understanding, consistently following and documenting the processes and procedures you have in place to minimize the risk of contamination of food.
Let’s take a more in-depth look at what your system would look like.
Commitment
The first step in creating your Food Safety Management System is to have a commitment to food safety. No matter what your brands message is your team needs to understand that without food safety you cannot provide a consistent message to your customers. This starts from the top down. When team members think the “bottom line” and sales is all you care about food safety will not be a priority. Unfortunately, the two go hand in hand.
SOP’s
Next establish your Standard Operating Procedures (SOP’s). This would include; your purchasing program that ensures your food is from a safe source, personal hygiene program, employee illness, cleaning and sanitizing program, how your facility avoids cross contamination, and establishing time and temperature controls to avoid bacterial growth. The person writing the SOP’s need to have a good understanding of food safety and the current practices and procedures of the facility. This is the core of preventing contamination to food.
Hazard Analysis
After your SOP’s are established you must look at every menu item and determine where a biological hazard could occur. These are called critical control points. In a Maryland retail food facility this would be steps in the process like cooking, cooling, reheating and hot holding. Again, the person doing the hazard analysis must have a good understanding of food safety risks. There are special considerations when the facility does certain practices like; using time as a public health control, cooks using sous vide, does any reduced oxygen packaging, uses additives or preservatives, cures food like bacon, displays seafood, squeezes juice or offers live shellfish in a display like a lobster tank.
Food Process Charts
Using data from the Hazard Analysis, create the food process charts. The Department of Health and Mental Hygiene offers four methods of creating charts. I prefer to use method #2. I feel that it is the easiest for food handlers to understand and follow along. For every CCP identified in the Hazard Analysis you must list the critical limit, how monitoring will take place, what corrective action you should take if there is a deviation in the critical limit and how will you verify the monitoring took place.
Training
Congratulations! You now have a HACCP plan. Now we need to make sure that team members are on the same page. That is where training come in. Training should be job specific and ongoing. Divide your facility into stations, for instance, prep, expo, servers, warewashing, etc. Review your SOP’s and make sure you include all necessary points in the training. Remember, everyone in your facility should be trained in personal hygiene and employee illness. Training can be computer based, group, one on one or a combination. I believe the best training starts with computer-based or group training and then one on one with a qualified team member providing the training. During training, be sure to correct the team member when doing something incorrectly. This can be done gently and politely but now is not the time to worry about hurt feelings.
Monitoring and Verification
Our system would not be complete without making sure that it is working. We do this through monitoring the critical limits established in the food charts and monitoring team members to ensure that all SOP’s are being followed as well. Monitoring is an action, for instance, it could be a visual observation or actually taking a temperature reading of cooked food. Verification occurs when monitoring is documented through charts and logs. The team member performing the task documents the result. Managers must review these logs and documents to ensure the system is working the way it should.
For instance, if a team member had to cook the chicken longer than the procedure states they would document this as a corrective action. Managers then review the corrective action documents and can then investigate why the corrective action had to be taken. Perhaps, they deep fryer is not working correctly, or the team member placed too much chicken at one time in the basket. Management can make corrections by either repairing equipment or retraining the team member.
Revise
When you make menu, equipment or structural changes the entire system needs to be reevaluated. Maryland requires your HACCP be revised every 5 years or when significant changes have taken place.

